在使用antd-vue版的table表格二次嵌套自定义组件时,原以为用<slot />插槽的方式就可以引入父级的所有子元素,结果根本不显示。
/ 前端
修改的新数组,原始数组也跟着改变了
分类:前端来源:站内 最近更新:2020-09-22 09:09:43浏览:1096留言:0
我们处理数组相关操作时经常会遇到复制一个新的数组后,修改新数组,老数组也跟着改变了。所以这次我们就来聊聊“地址引用”。
先看下面一个js片段:
let arr = [
{
title: "aa",
},
{
title: "bb",
},
];
let reArr = [...arr]; //是个新数组
let result = reArr.map((item) => {
//map 也会生成新数组,正常情况下arr,reArr,result都是新数组,不相互干扰
item.title += "--first";
return item;
});
console.log(arr, reArr, result); //结果……写过C语言的开发,肯定知道指针的概念,很不幸JS里没有,可能唯一能算作指针的就是this了。我们对数组的指针有“地址引用”的说法。请看下图:
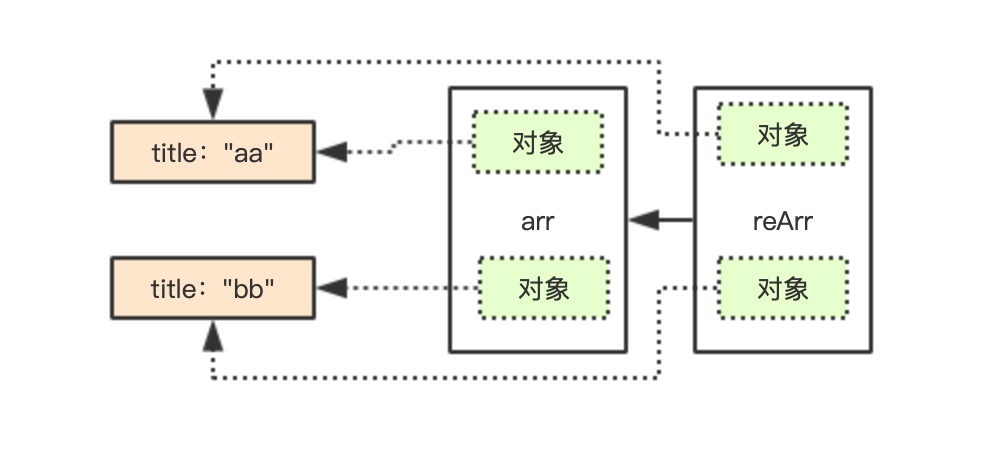
语法reArr=[...arr]是浅拷贝,只是拷贝了数组arr每个对象的位置属性,真实的数据源是在橙色的数据存储空间内,当我们修改对象值的时候,其实是修改了橙色的数据源,两个数组的共用对象值,因此arr也跟着改变了。
理解地址引用,我们就有解决方案了,让新的数组要深拷贝,或者完全生成一个新的数组,数据源也是新的。
方法一:
把二级数据对象,从重新生成,生成新的地址引用
let result = reArr.map((item) => {
return { ...item, title: item.title + "--first" }; //新的地址索引
}); 缺点:只求修改两级,多级要多级在深拷贝,但是是最合理的处理方式,推荐
方法二:
直接复制一个全新的数组对象,把数组先生成JSON字符串,再转回数组
let reArr = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(arr)); //是个新数组
let result = reArr.map((item) => {
item.title += "--first";
return item;
}); 优点:简单粗暴,个人不喜欢;
扩展:
很多数组的方法都是 浅拷贝,不如之前经常用的数组常用方法,map,filter,splice,concat等都是浅拷贝,当数组是二位数组的时候,就要考虑深拷贝了。推荐全能的深拷贝常用函数:
"use strict";
// Method that will return the data type for any structure passed to it
function getDataType(data) {
// Use the objects toString method on the data.
// This will return something like [object String]
// Then we use .slice to grab the last portion of it (in this case the "string" bit)
return Object.prototype.toString.call(data).slice(8, -1);
}
// Create a method to detect whether an object contains a circular reference
function isCyclic(data) {
// Create an array that will store the nodes of the array that have already been iterated over
var seenObjects = [];
function detect(data) {
// If the data pass is an object
if (data && getDataType(data) === "Object") {
// If the data is already in the seen nodes array then we know there is a circular reference
// Therefore return true
if (seenObjects.indexOf(data) !== -1) {
return true;
}
// Add the data to the seen objects array
seenObjects.push(data);
// Begin iterating through the data passed to the method
for (var key in data) {
// Recall this method with the objects key
if (
Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(data, key) === true &&
detect(data[key])
) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// Return the method
return detect(data);
}
export default function deepClone(data) {
// If the data is null or undefined then we return undefined
if (data === null || data === undefined) {
return undefined;
}
// Get the data type and store it
var dataType = getDataType(data);
// If the data passed is a date object
if (dataType === "Date") {
// Create a new date object and set the time to what it was previously
var dataDate = data;
var clonedDate = new Date();
clonedDate.setTime(dataDate.getTime());
return clonedDate;
}
// If the data passed is an object
if (dataType === "Object") {
// Check for circular references, if there are then we just return the un-cloned data.
if (isCyclic(data) === true) {
return data;
}
// Create a new object that will store our copied data
var copiedObject = {};
// Iterate over the objects keys
for (var key in data) {
// Clone the keys of each of the objects so that we can deeply copy and nested data structures
// For example if an object has a key value that is an array
// Add this cloned key value to the copiedObject we created earlier
copiedObject[key] = deepClone(data[key]);
}
// Return the deeply copied object
return copiedObject;
}
// If the data is an array
if (dataType === "Array") {
// Create a new array that will have no references to the one we want to copy
var copiedArray = [];
var dataArray = data;
// Iterate over the arrays elements
for (var i = 0; i < dataArray.length; i++) {
// Push the arrays elements to this new array
// First recall this method with the elements
// This is so arrays of objects and other nested data structures get correctly cloned.
copiedArray.push(deepClone(dataArray[i]));
}
// Return the cloned array
return copiedArray;
}
// If it's any other data type like a string or number, they don't need cloning so we just return them
else {
return data;
}
}上一篇:了解前端分分钟,一入前端毁终生
下一篇:前端脚手架如何搭建
0
发表评论
评论列表(0)
- 暂时没有留言
热门
Antd vue table表格二次嵌套slot插槽不显示问题
2020-09-17 18:28:204384typescript中implements和extend继承的区别
2022-08-02 18:36:353581微信小程序Eslint配置中需添加全局方法
2022-11-30 20:56:413410vue-devtools 仓库build报错
2020-11-03 12:01:112752
